Reducing water usage (Part 2)
Posted by Wesley on
Measuring the amount of water coming out, the simple way
Softrong has touted their faucets' water-saving feature prominently, and I noted that it felt like it was working. But to see if it was indeed the case, I made actual measurements. No fancy equipment were necessary - just a stopwatch and a water jug would do as you can see here. After repeating and averaging, these are the results.
| Shower Head Name |
Room | Consumption (ml/sec) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% | 50% | 25% | 13% | ||
| (Default Head) | 1 | 202 | 180 | 124 | 84 |
| Softrong SH-50 | 109 | 106 | 82 | 35 | |
| (Default Head) | 2 | 200 | 199 | 177 | 124 |
| Softrong SH-50 | 101 | 101 | 99 | 75 | |
| Kitchen Faucet Name |
Mode | Consumption (ml/sec) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% | 50% | ||
| (Default Faucet) | Default | 120 | 100 |
| Softrong SKJ-60 | Spread | 49 | 44 |
| Middle | 96 | 76 | |
| Focused | 107 | 80 | |
In any case, the replacements were definitely using less water if they were used for a same duration. Now I needed to see if this translated to tangible reduction in metered usage.
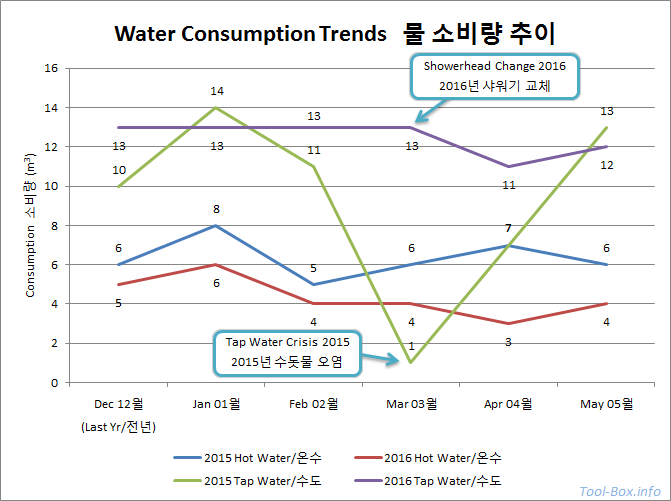
Comparison of the water consumption trends between 2015 and 2016
And here are the results. Note that, between late February and early April of 2015, Naju Bitgaram City suffered widespread contamination of tap water. It became unfit for most uses in heavily affected areas, and the city decided to not meter the water use during the affected period. However, the hot water use was still metered as you were paying the costs of heating the water, not the water use itself.
Taking this into account, tap water use hovered steadily around 13m3 (13,000L) throughout the year until the faucets were replaced. I saw a drop of around 1 to 2m3 afterwards. In the case of hot water, there had been about 1m3 reduction year-over-year (from 6m3 to 5m3 on average), but it dropped further on a similar scale as the tap water after the replacement.
Here, tap water costs about US$0.75/m3 and hot water, US$4.20/m3. So the reduction of 1m3 seen here equates to about 5 dollars in savings per month. The shower heads cost US$20 each and the kitchen faucet, US$30 - a total of US$70. That means it would only take just over a year to recover the upgrade costs. Even though the water use didn't fall dramatically, the new faucets still turned out to be good investments.