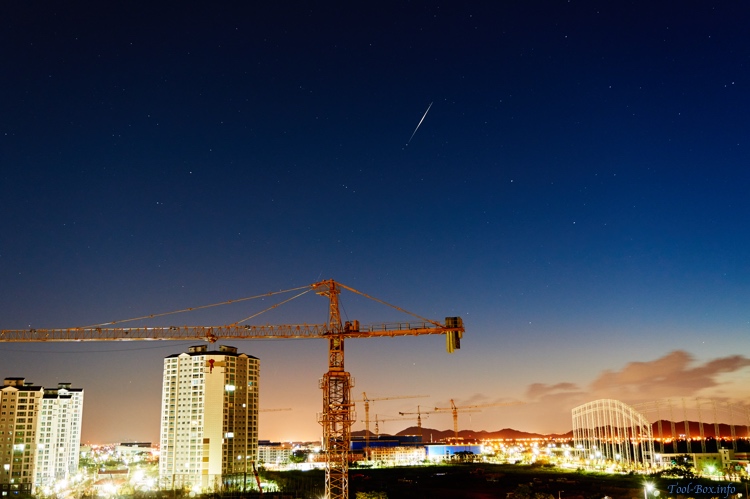
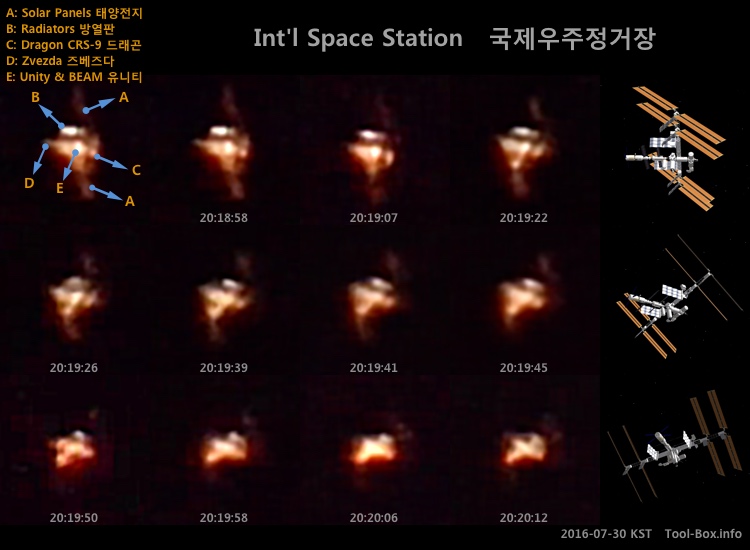
The streak of Iridium 60's flare
Posted by Wesley onIt's been more than two years since I talked about satellite flares here, but I now have something to show you. As you can see, I had a camera successfully capture the flares coming from an Iridium satellite for the first time. Past efforts used iPhones because I was focused in capturing the motion of the flares. In this photo, the ever-growing Naju Bitgaram City provided a colourful backdrop.
Device: Sony A5000 + SELP1650 (E PZ 16–50 mm F3.5–5.6 OSS)
Settings: 24mm - ISO 400 - 20s - f/4.5
Filters: None
Time: 2016-08-30 05:06 KST
Location: Naju, Korea