Checking out iPhone 7's physical changes
Posted by Wesley on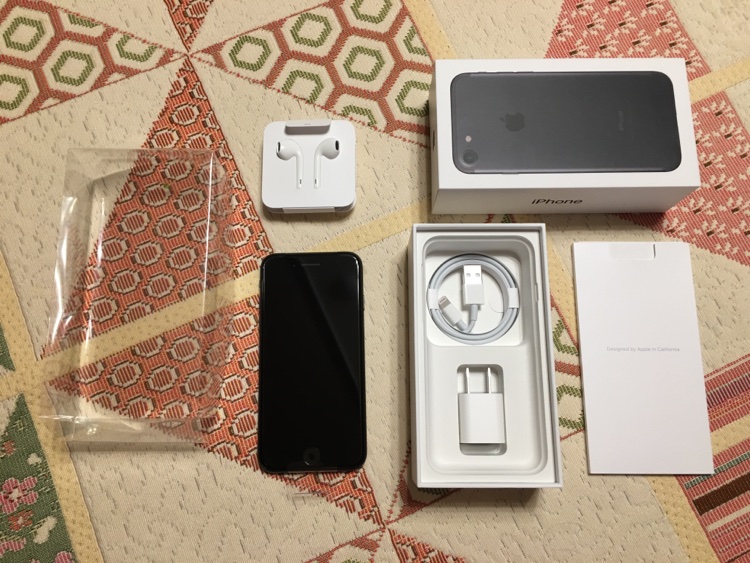
Contents of the iPhone 7 package
As far as changes go, iPhone 7 is doing a big jump we've come to expect when the major number changes (e.g. iPhone 5S to iPhone 6). It just happens to be that Apple was happy to keep the general shape and size for the third generation. Personally, this seems like Apple is happy with these design decisions instead of being lazy. After all, Original iPhone style survived three generations as well until thinner design became feasible.
In any case, the packaging of the iPhone 7 is also largely the same as the previous 4.7" iPhones. Two major differences, other than the phone itself, are the photo of the iPhone on the box and the bundled EarPod earphones using the Lightning connector instead of the 3.5mm earphone jack. 3.5mm to Lightning adapter is included for those who need to use the existing earphones.
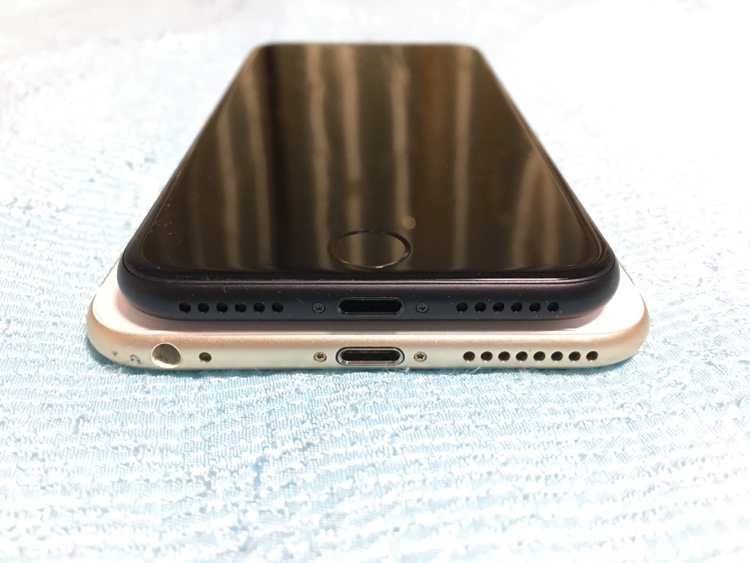

Bottom area: iPhone 7 (top) and iPhone 6 Plus (bottom)
Speaking of the earphone jack, iPhone 7 indeed no longer has one as you can see here. This has been the source of much online drama, but I expect it to simmer down as time goes on, much like when Lightning connector itself was introduced with iPhone 5.